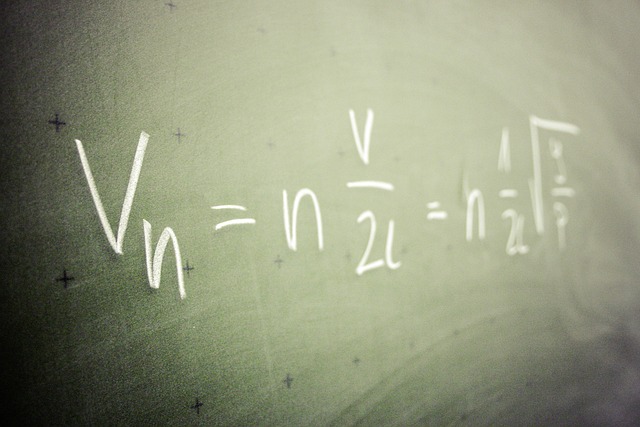Where Exploration Leads to Academic Excellence
A Knowledge Hub by Rahul Anand
Mathematical Marvels: Insights from the Field
Ramanujan Junior Researchers Programme: A New Era of Math Research
Discover how the Ramanujan Junior Researchers Programme is fostering India-UK collaboration in theoretical physics and mathematics.
Experiential Math Learning: Curing Math Phobia in India
Experiential math learning is transforming Indian education. Discover how Ramanujan Math Parks and Atal Tinkering Labs are making math hands-on.
The Power of Banach Limits
Explore the fascinating world of the Banach Limit, a mathematical tool that extends the concept of limits beyond convergent sequences, assigning a limit value to sequences that might otherwise seem ‘limitless’.
Understanding Stochastic Convergence
Explore the intricacies of Stochastic convergence, a vital concept in probability theory. Learn about the different types and their applications in statistics and stochastic processes.
Understanding the Convergent Matrix
A **Convergent Matrix** is a square matrix that converges to the zero matrix when raised to successive powers. This article explores the properties of these matrices and their importance in iterative methods.
Category Theory Limits
Category theory limits provide a unified way to describe and relate various mathematical structures. This post explains how category theory limits are fundamental tools for understanding complex mathematical ideas.
Limit Superior and Inferior
Understand Limit Superior and Inferior: Learn how these concepts define the eventual bounds of sequences and functions, and their importance in mathematical analysis.
The Diverse Types of Convergence in Mathematics
Understanding the different **types of convergence** is essential in mathematics. From sequences and series to functions, this post explores the various modes of convergence.
Calculus Castle
Proving Mathematical Propositions: Direct Indirect and Other Methods
Learn various methods for proving mathematical statements including direct proof indirect proof (contradiction and contrapositive) proof by cases and mathematical induction. Explore examples and applications.
Navigating the CBSE Board Exams 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
Conquer the CBSE Board Exams 2025 with our guide! Learn effective study strategies, time management tips, and overcome exam anxiety for success.
Find the limit: \( \lim_{x \to 3} (2x + 5) \)
Find \( \lim_{x \to 3} (2x + 5) \) Solution:To solve this limit, we substitute the value of \( x \) directly because the function is continuous at \( x = 3 \).\( \lim_{x \to 3} (2x + 5) = 2(3) + 5 = 6 + 5 = 11 \)
Morning Refresher – 5 Basic Problems in Limits to Boost Your Mind
5 Basic Problems on Limits just to refresh your mind. Problem 1 Find the limit: \( \lim_{x \to 2} (3x – 4) \) Solution: To solve this limit, we substitute the value of \(x\) directly because the function is continuous at \(x = 2\). \[ \lim_{x \to 2} (3x – 4) = 3(2) -…
THEOREM# \( \lim_{\theta\to0} \dfrac{sinθ}{θ} \) = 1
We have \( \lim_{\theta\to0} { \sin\theta \over \theta } \) = 1 Consider the below diagram. We have r = radius of the circle.A = centre of the circle.The sector ⌔ formed by the arc BD subtends an angle θ at the centre. Case 1 : θ > 0 i.e. θ is +ve Let 0 ≤ θ ≤ \(…
Theorem# \( \lim_{x \to a} { x^n – a^n \over x – a } = na^{n-1} \)
To prove : lim\( _{x \to a} { x^n – a^n \over x – a } = na^{n-1} \) where n is a rational number Proof: Let \( x = a + h \) Then as \(x \to a \), we have \(h \to 0 \) Now, \( \lim_{x \to a} { x^n – a^n \over x – a } = \lim_{h \to 0} { (a…
Theorem# Limit of tanθ as θ → 0
Proof : We have, lim\(_{θ\to 0} { \dfrac {\mathrm tan \mathrm θ}{ \mathrm θ} } \) = lim\(_{θ\to 0} { \dfrac {\mathrm \sin \mathrm θ} {\mathrm θ \mathrm \cos\mathrm θ} } \) \( \{∵ \tan\theta = \dfrac…
Theorem# Limit of cosθ as θ → 0
As θ → 0, we have cosθ → 1 Proof : When θ = 0, We have, lim\(_{θ\to 0} \cos \)θ = cos0 = 1 { ∵ cos0 = 1 } Hence, lim\(_{θ\to 0} \cos \)θ = 1
Derivative of \(\mathsf { x^{n} }\) using the First Principle
Let y = \(\mathsf {x^{n} }\) ∴ y + δy = \(\mathsf { {(x + δx)^{n}} }\) ∴ δy = y + δy – y = \(\mathsf { (x + δx)^{n} }\) – \(\mathsf { x^{n} }\) or δy = \(\mathsf { [\text{ }^{n}C_0 x^{n}{(δx)}^{0} }\) + \(\mathsf {\text{ }^{n}C_1 x^{n-1}{(δx)}^{1}}\) + \(\mathsf…
Derivative of \({e}^x\) using First Principle
Derivative of \({e}^x\) using the First Principle Let \(y\) = \({e}^x\)∴ \(y + δy\) = \({e}^{x + δx}\)∴ \(δy\) = \({e}^{x + δx}\) – \({e}^x\)or \(δy\) = \({e}^{x}\) . \( [ {e}^{δx} – 1 ]\)Dividing each side by δx </h3>or \(\dfrac {δy}{δx}\) = \( \dfrac { {e}^{x}…
Insight into the Laws of Physics
IIT JEE Mechanics Numericals
Test skills in Newton’s laws and motion.
Find all meet instants that match vertical heights with gravity
Account for g=9.8 m/s² and the start-time offset.
Find the coasting interval to plan multiphase travel efficiently
Use three phases: accelerate, coast, brake to rest at a set distance.
Compute time and acceleration by integrating position dependent velocity v(x)
Apply calculus carefully; watch units and evaluation limits.
When do they meet? Equations to analyze relative motion precisely
Translate each car’s motion into position functions; solve intersection or show none.
Find arrival time by calculus to solve 1D kinematics accurately
Integrate a(t) to v(t) and x(t), then locate the first positive root.
IIT JEE Optics Numericals
Excel in ray optics problems.
IIT JEE Gravitation Numericals
Solve gravitation based numericals.
NUMERICAL SOLUTIONS IN PHYSICS
Understanding Newton’s Law of Gravitation: A Detailed Explanation and Example
Learn how Newton’s Law of Gravitation describes the force of attraction between masses. This example calculation demonstrates the formula in action.
Solving Projectile Motion: Finding Maximum Height and Time of Flight Using a Quadratic Equation
Learn how to solve projectile motion problems using quadratic equations. Find the maximum height and time of flight for a projectile launched at a 45-degree angle.
Navigating the CBSE Board Exams 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
Conquer the CBSE Board Exams 2025 with our guide! Learn effective study strategies, time management tips, and overcome exam anxiety for success.
Swimmer in a River: RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE MOTION NUMERICAL PROBLEMS
A swimmer is crossing a river that flows at 2 m/s. The swimmer’s speed relative to the water is 4 m/s.
Determine the swimmer’s speed relative to the riverbank (absolute motion) when swimming directly downstream.
Determine the swimmer’s speed relative to the riverbank w…
A Boat is moving downstream on a river. Determine the speed of the boat relative to the riverbank (RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE MOTION NUMERICAL PROBLEMS)
A boat is moving downstream on a river. The river flows at a speed of 3 m/s relative to the riverbank. The boat’s engine propels it at a speed of 7 m/s relative to the water.
Determine the speed of the boat relative to the riverbank (absolute motion).
If the boat turns…
Drive, Walk, Refuel: Find Displacement, Time & Velocity
You drive a car on a straight road at a constant speed of 70 km/h for a distance of 8.4 km, after which the car runs out of fuel. You then walk a further distance of 2 km for 30 minutes to reach the gas station. a) What is the total displacement from the beginning of yo…
Numerical Examples in Motion in One Dimension – Kinematics
These problems encompass a variety of scenarios involving motion in one dimension, designed to reinforce the understanding of key concepts such as constant velocity, acceleration, deceleration, and the equations of motion.
Atom to Atom: Insights from the Chemical Universe
Olfactory Indicators
Olfactory indicators, also known as smell indicators or odor indicators, are substances that change their smell in the presence of certain chemicals or conditions. They are commonly used in chemistry experiments to detect the presence or absence of specific gases or to …
Understanding Chemical Reactions and Equations
Get ready to embark on a journey through the fascinating realm of chemical reactions and equations, where every reaction is a symphony of atoms dancing to the tunes of nature.
From Kaṇāda to Rutherford: Tracing the Evolution of Atomic Theory
The evolution of atomic theory is a long and winding road that has been travelled by some of the greatest minds in history. It began with the ancient Indians in 600 BC who gave the concept of “Parmanu” to Greeks who first proposed that matter was made up of tiny, indivi…
10 Examples of combination reactions
1. The reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to form water: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O 2. The reaction between iron and sulfur to form iron sulfide: Fe + S → FeS 3. The reaction between magnesium and oxygen to form magnesium oxide: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO 4. The reaction between…
Periodic table
A periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The periodic table is one of the most important tools in chemistry, and it is used by scientists and engineers…
Chemical Fertilizer vs. Organic Fertilizer
A popular topic among agriculture specialists and home gardeners these days is the furore on organic fertilizer vs. chemical fertilizer. Now each fertilizer certainly has its pros and cons, but before we delve deeper into that, let us first make a few…
Liquid Organic Fertilizer
Using organic fertilizers is a widely accepted practice in the agricultural industry. Farmers use them to cultivate their fields and row crops, winemakers utilize them for growing grapes, and horticulturists apply a liberal dose of these during the landscaping of…
Characteristics of a chemical reaction.
A chemical reaction generally has one or more of the below-mentioned characteristics. Change in state Change in colour Evolution of gas Change in temperature Appearance of light Formation of Precipitate 1> Change in stateCertain chemical reactions are featured with a…
Life’s Mysteries Revealed: Exploring Biology
Scientists Develop Antivenom Treatment to Combat Snakebites
Scientists are working to develop antivenom treatment using nanobodies from camelids, offering a promising solution to snakebites and improving treatment. You’ll learn to develop antivenom treatment with this new approach.
Mirror Life Risks: Scientists Confront Synthetic Biology Dangers
Mirror life risks are a growing concern as scientists explore synthetic cells. Experts are discussing how to manage the potential dangers.
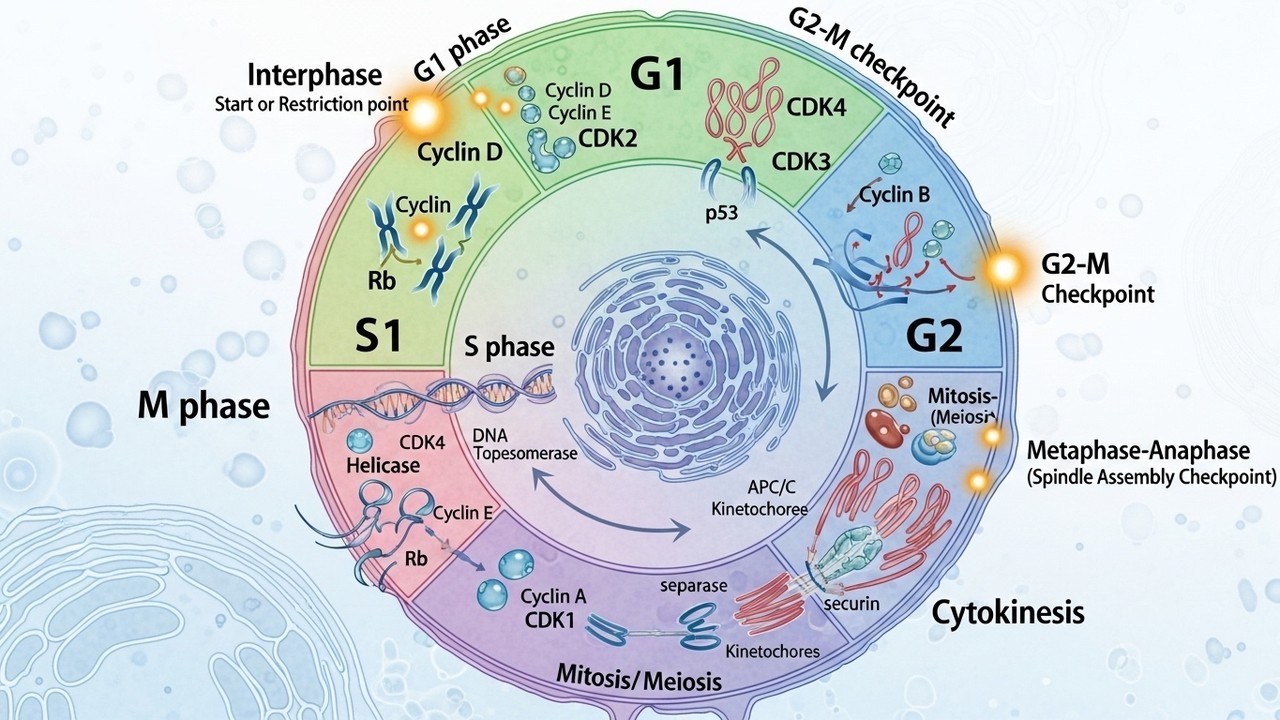
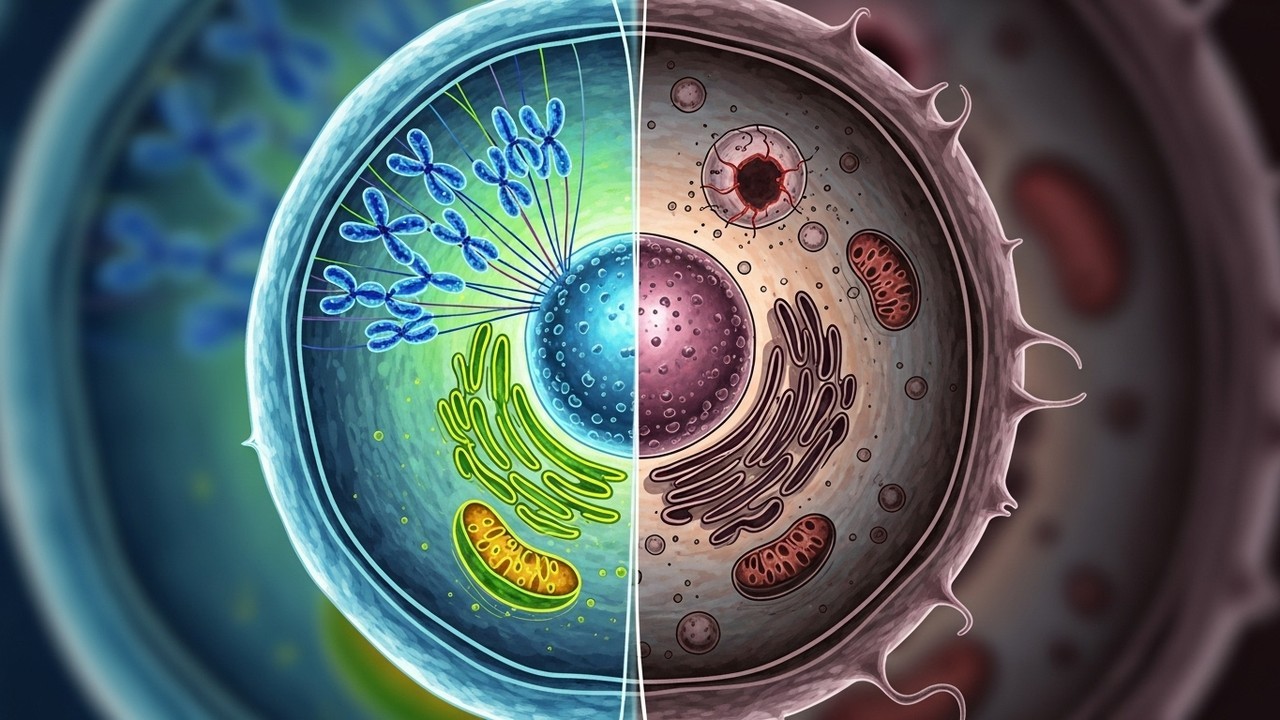
Cell Cycle Regulation and Checkpoints in Advanced Cell Biology
Understand how checkpoints ensure proper division and prevent mutations.
Stem Cell Division and Differentiation in Advanced Biology
Understand how stem cells decide between renewal and specialization.
Balancing Apoptosis and Cell Division in Multicellular Organisms
Discover why balance between life and death of cells is essential.
Mitotic Signaling Pathways and Their Role in Cell Division
Learn how signaling cascades control mitosis progression.
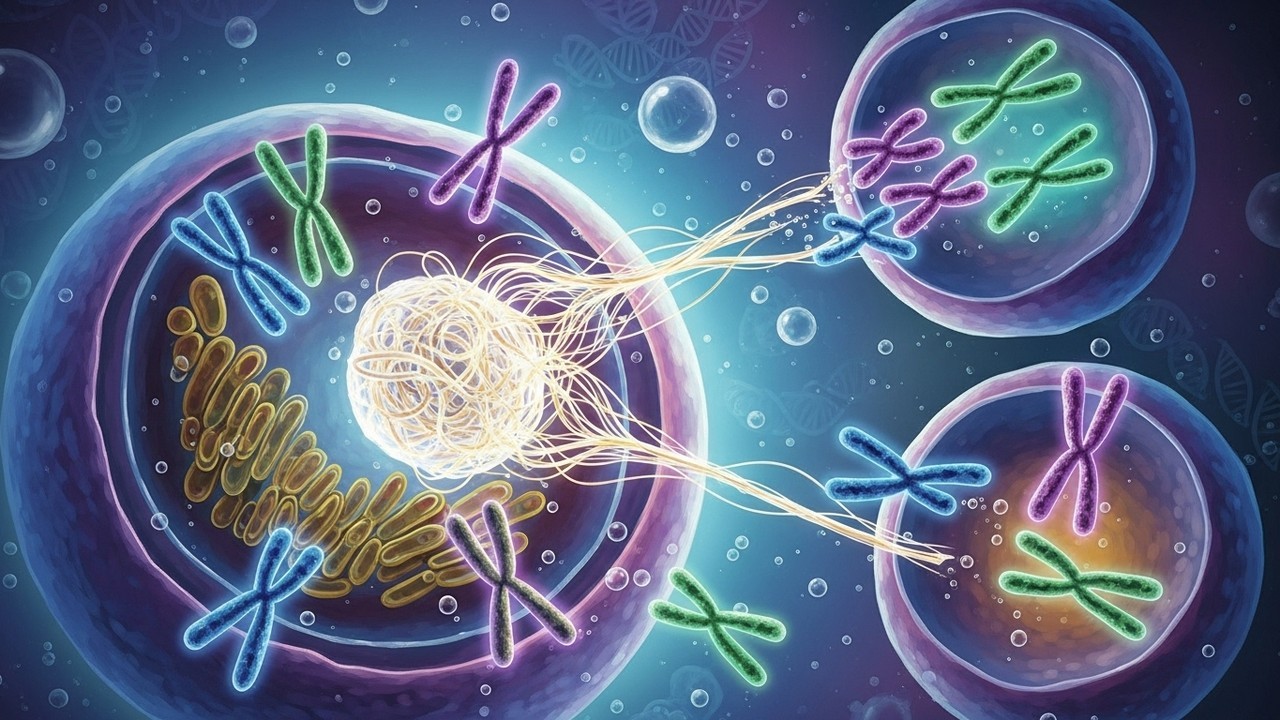
Meiotic Errors and Their Role in Genetic Disorders
Explore how meiotic errors cause Down syndrome and other conditions.
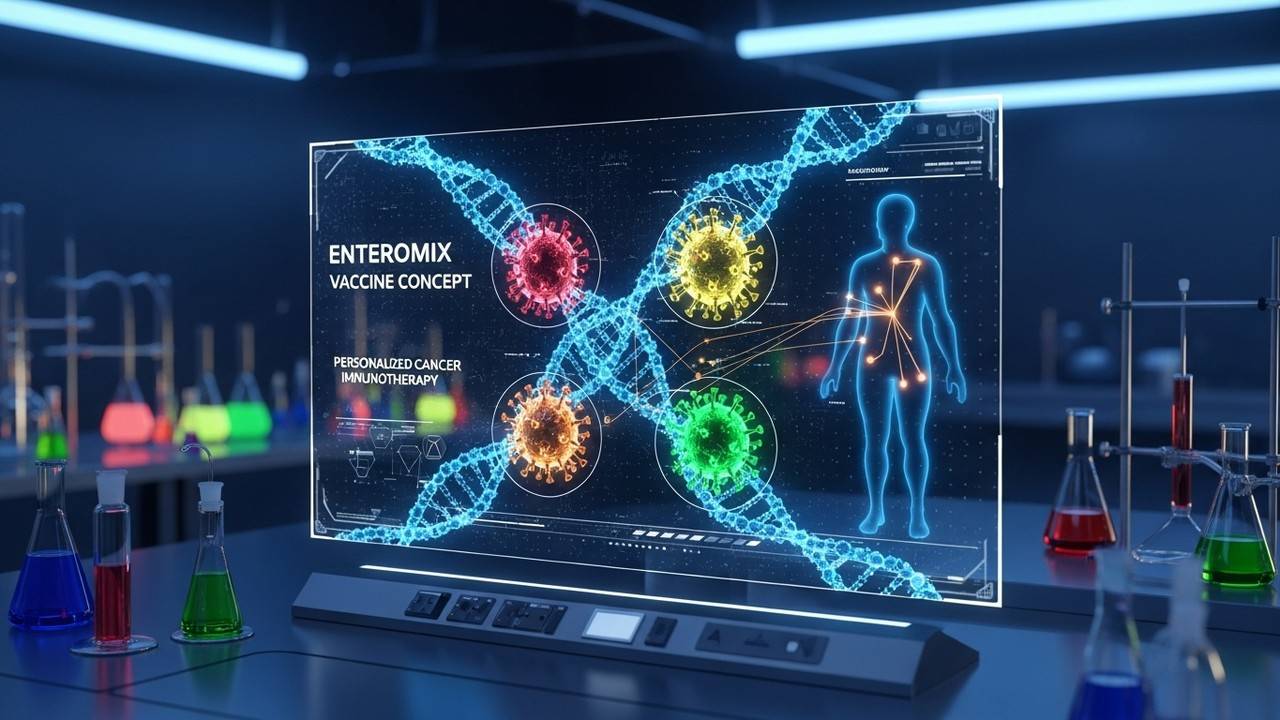
EnteroMix and the Rise of a personalised cancer vaccine
EnteroMix and the idea of a personalised cancer vaccine signals a potential shift in cancer care, but requires rigorous validation.