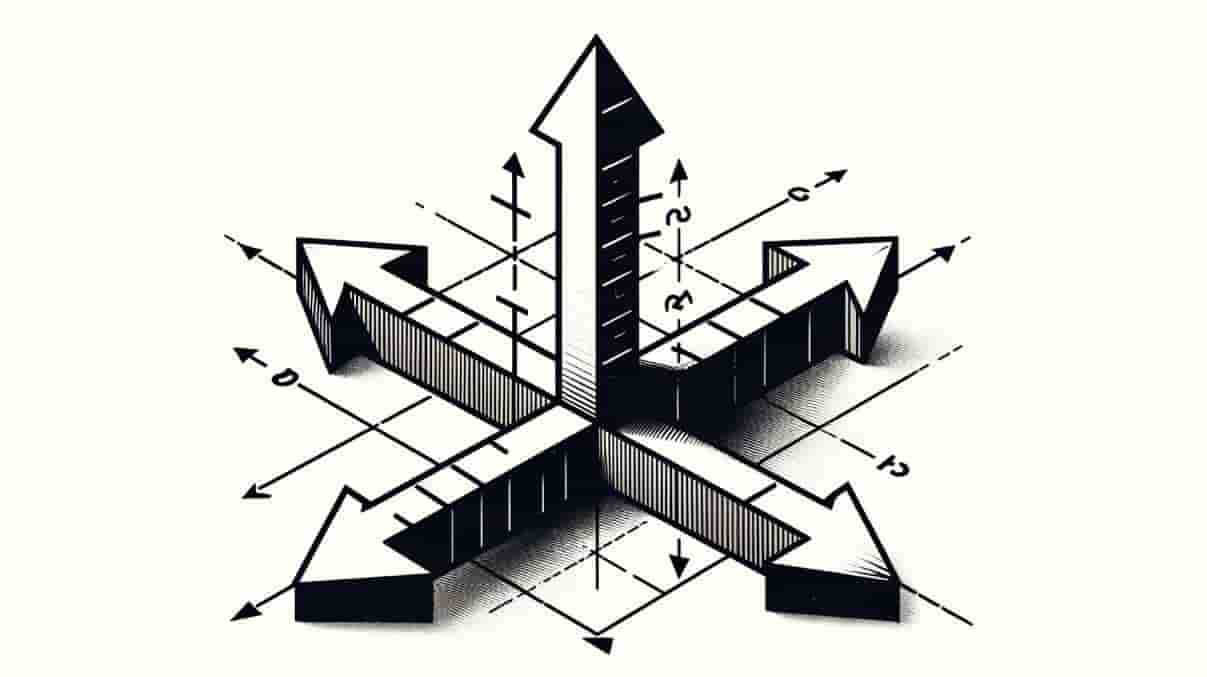
In physics and geometry, the concept of “three dimensions” refers to a spatial framework necessary to describe the position or location of an object fully. Each dimension provides a unique axis that, together with the others, can describe any point in space. Here’s a breakdown of the three dimensions typically used:
We also published:
Scientific Notations1. X-Axis (First Dimension)
- This is often thought of as the horizontal dimension.
- In a Cartesian coordinate system, it typically defines width or length.
2. Y-Axis (Second Dimension)
- This axis is perpendicular to the x-axis.
- In a Cartesian coordinate system, it typically defines height or breadth when considered in a two-dimensional plane along with the x-axis.
3. Z-Axis (Third Dimension)
- The z-axis is perpendicular to both the x-axis and the y-axis, completing the three-dimensional framework.
- It adds depth to the spatial configuration, allowing for a full three-dimensional perspective.
These three axes intersect at a common point called the origin, and each axis can be thought of as a number line. In three-dimensional space, you can measure distances along these axes and use them to specify any location in space via coordinates. This three-dimensional space is foundational in many areas of science and engineering, allowing for the modelling and analysis of physical phenomena and structures in a more realistic manner that matches our observations of the natural world.
Latest Articles from Science and Technology Websites
“Watch a tripod robot test its asteroid leaping skills” – Popular Science Discover the latest advancements in robotic mobility with a focus on space exploration and asteroid surface analysis.
“How AI mathematicians might finally deliver human-level reasoning” – New Scientist Explore how artificial intelligence is being developed to tackle complex mathematical problems and mimic human reasoning.
“What happens when climate change and the mental-health crisis collide?” – Nature Read about the intertwined challenges of climate change and mental health, and the necessary steps to address these issues.
“Is robotics about to have its own ChatGPT moment?” – MIT Technology Review Delve into the potential breakthroughs in robotics that could transform daily life and industrial processes.
“Why counting octopus ‘rings’ is crucial” – Scientific American Learn how researchers are using innovative methods to age octopuses and assess environmental impact on their growth.




0 Comments