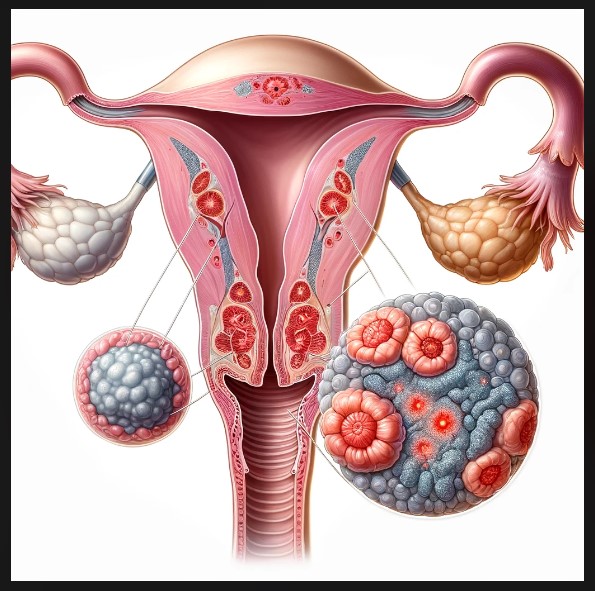
General information about Cervical cancer
ADVERTISEMENT

General information about Cervical cancer

The evolution of atomic theory is a long and winding road that has been travelled by some of the greatest minds in history. It began with the ancient Indians in 600 BC who gave the concept of “Parmanu” to Greeks who first proposed that matter was made up of tiny, indivisible particles. The 19th and 20th centuries saw significant advances in our understanding of atoms.
Information about Random Phenomena

A random event refers to an unpredictable occurrence that has no discernible pattern or predetermined outcome. It is an event whose outcome cannot be reliably predicted or determined based on prior information or knowledge. Random events are commonly encountered in...
For a binary representation of a number, the Least Significant Bit (LSB) is the binary 1s place or simply the rightmost bit. The Most Significant Bit (MSB) is the highest-order place of the binary integer or the left-most bit. Consider the binary...
A Type in programming is used to refer to the data type such as int, char, or user-defined structured data types. A Static type programming language is one where the data type of the variable is known before the execution of the program. This is...
A strongly typed system is one that does not allow the conversion of data types during execution, in case there is a mismatch. For instance, if “18” is presented for an integer variable instead of 18, the system raises an error. Perl, Ruby, Python and Pascal are...