The Number System Fundamentals are the bedrock of mathematical understanding, a topic essential for anyone embarking on a journey through mathematics, from the elementary school level to the advanced realms of calculus and beyond. The ability to classify and manipulate numbers is a foundational skill that underpins all advanced mathematical concepts. This lesson will delve into the intricacies of number systems, exploring the various classifications, from the familiar natural numbers to the more abstract complex numbers. We'll dissect the properties of each number set, providing a comprehensive overview that will empower you to approach mathematical problems with confidence and clarity. Understanding the nuances of the Number System Fundamentals is essential.
On This Page
Number System Overview
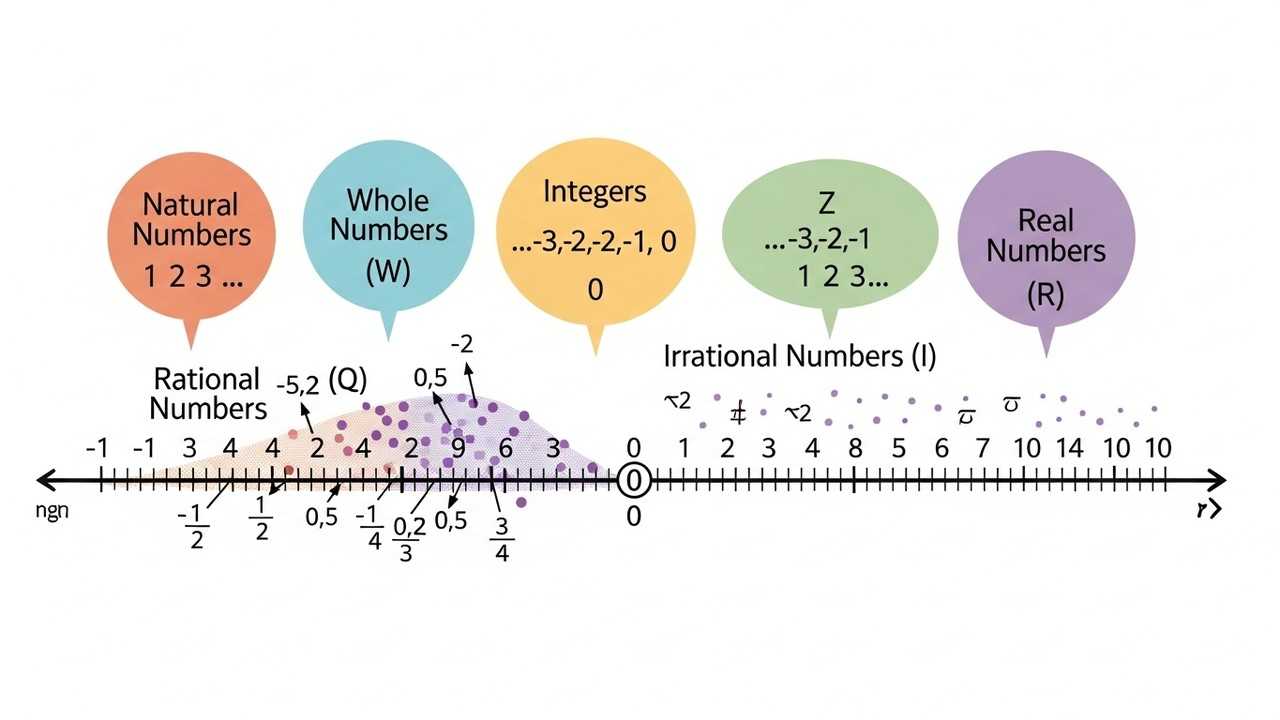
The world of numbers is vast and varied, and understanding its structure is paramount. We begin by defining the fundamental sets of numbers: Natural numbers (ℕ), Whole numbers (W), Integers (ℤ), Rational numbers (ℚ), Irrational numbers, Real numbers (ℝ), and Complex numbers (ℂ). Each set has unique properties and plays a crucial role in different areas of mathematics. The Number System Fundamentals are essential for performing calculations and solving equations. The relationships between these sets form a hierarchical structure, with each set building upon the previous ones.
Natural Numbers (ℕ)
Natural numbers are the counting numbers: {1, 2, 3, ...}. They are the most basic set and are used for counting objects. Natural numbers are the foundation upon which other number sets are built. The definition of natural numbers is the starting point. These numbers are the most intuitive and are the first numbers we learn as children. They are always positive and do not include zero.
Whole Numbers and Integers
Whole numbers extend natural numbers by including zero: {0, 1, 2, ...}. Integers encompass both positive and negative whole numbers: {..., -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ...}. Understanding the difference between whole numbers and integers is critical for solving equations. The inclusion of zero is crucial for defining certain mathematical operations and concepts. Integers are essential for representing quantities that can be negative, such as temperature or debt. The concept of integers introduces the idea of additive inverses.
Rational Numbers (ℚ)
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction ## \dfrac{p}{q}##, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. This set includes all integers and fractions. The ability to convert between fractions, decimals, and percentages is a key skill. Rational numbers represent the ability to divide a whole into equal parts. Understanding rational numbers is essential for solving equations involving fractions and decimals. Decimals can be terminating or repeating, which is a key identifier.
Irrational and Real Numbers
Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers. Examples include √2 and π. Real numbers comprise both rational and irrational numbers, representing all points on a number line. The combination of rational and irrational numbers forms the set of real numbers. The number line is a visual representation of real numbers, crucial for understanding inequalities. The concept of irrational numbers expands our understanding of the number system. These are the numbers that can't be written as fractions.
Imaginary and Complex Numbers
Imaginary numbers involve the imaginary unit i, where ##i = \sqrt{-1}##. Complex numbers are of the form ##z = x + iy##, where x and y are real numbers. Complex numbers extend the real number system, providing solutions to equations that have no real roots. Complex numbers have both a real and an imaginary part. Complex numbers are critical for advanced mathematical applications, including electrical engineering. The Argand diagram is a visual tool for representing complex numbers.
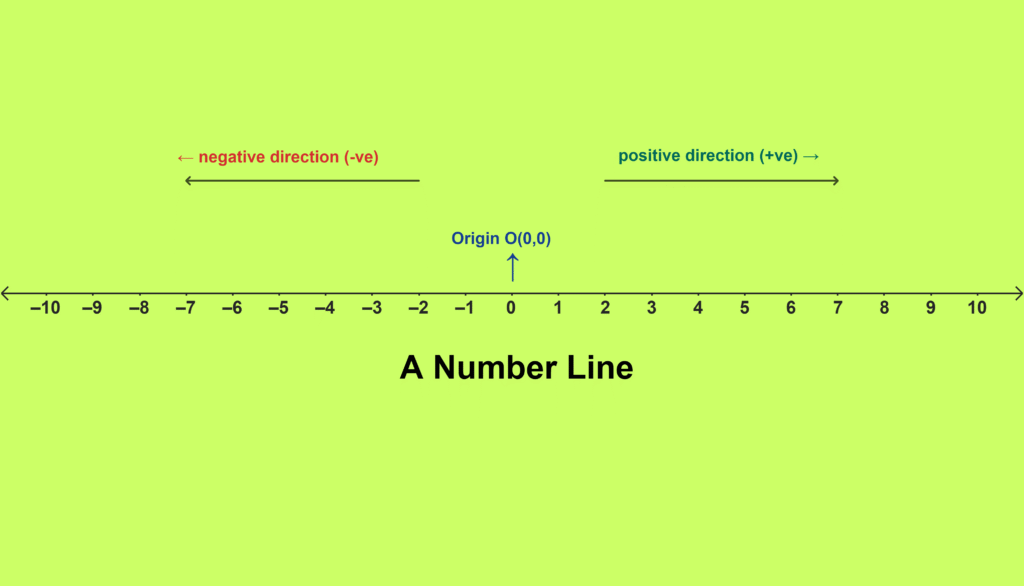
Number Line Representation
The number line is a visual tool used to represent all real numbers. Each number is placed at its corresponding point on the line. The number line is a fundamental concept in mathematics. It helps in visualizing the ordering of numbers and understanding inequalities. The number line is essential for understanding the relative positions of numbers. The number line is a visual aid for understanding concepts. The number line is a critical tool for understanding mathematical concepts.
Importance in JEE Mathematics
A strong grasp of the Number System Fundamentals is crucial for success in JEE. Questions on number classification, properties, and applications appear frequently. The ability to quickly and accurately identify number types is essential for solving complex problems. JEE problems often involve manipulating different types of numbers. A solid understanding of the material is very important. JEE requires a deep understanding of these number system concepts.
Examples and Practice
Let's solidify our understanding with a few examples. Is ##\sqrt{9}## rational? Yes, because ##\sqrt{9} = 3##, which is an integer and can be expressed as ##\frac{3}{1}##. Is 0 a natural number? No, depending on the definition used, but in the context of JEE, 0 is not typically considered a natural number. The ability to classify numbers is a fundamental skill. These examples highlight the application of the definitions. Practicing these types of problems will help you get better.
Practice Problems
Identify whether each number is natural, whole, integer, rational, or irrational: 0, ##\frac{3}{4}##, -2, ##\sqrt{5}##, 0.333... Write the first five positive irrational numbers greater than 2. These problems are designed to test your understanding. The ability to classify numbers accurately is very important. These problems help in identifying the different types of numbers.
JEE-Specific Tips
In JEE, be prepared for trick questions that combine number classification with decimal expansions or properties of integers. Always double-check the definitions. Pay close attention to the details. Practice with a variety of problems. The ability to think critically is crucial. Understanding the nuances of the definitions is critical for JEE. The ability to identify the number is a must.
Problems and Quick Solutions
Problem 1: Classify ##\frac{22}{7}##.
Solution: Rational
Problem 2: Is -5 a whole number?
Solution: No
Problem 3: What type of number is π?
Solution: Irrational
Problem 4: Is 1.5 an integer?
Solution: No
Problem 5: Simplify ##\sqrt{4}## and classify.
Solution: 2, Rational
RESOURCES
- Fundamentals (Representing Digital Information 1): Number Systems
- 5 Number Systems, Conversions, and Codes | part of Electronic ...
- Number Systems Introduction - Decimal, Binary, Octal ...
- Number System in Maths
- Complex number fundamentals | Ep. 3 Lockdown live math - YouTube
- Fundamentals of Number System | PDF | Numbers | Real Number
- I'm having some trouble with understanding the binary number ...
- united states - How does the college course 101 numbering system ...
- Boxing Fundamentals: Understanding The Boxing Punch Number ...
- Quiz 4: The Real Number System Mathematics 700 Fundamentals ...






0 Comments