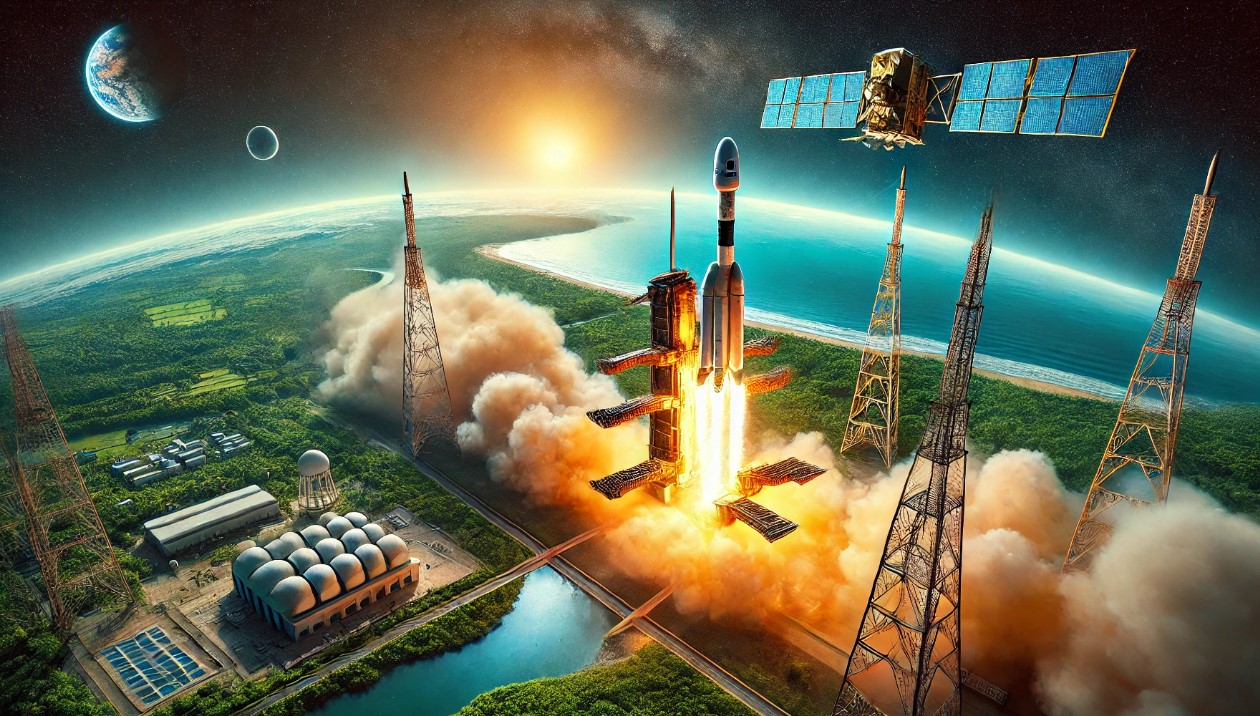
ISRO's SSLV-D3: Pioneering the Future of Satellite Launches
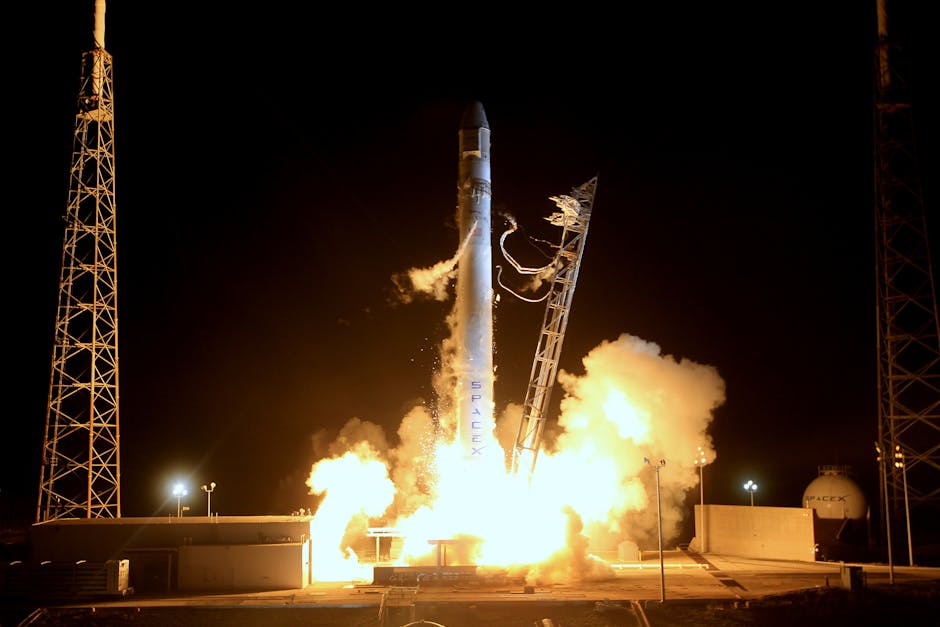
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has once again demonstrated its prowess in space technology with the successful launch of the SSLV-D3 rocket. On the morning of August 16, 2024, at precisely 9:17 AM, the ISRO's SSLV-D3 soared into the sky from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, carrying with it India's latest Earth Observation Satellite, EOS-8. This mission marks a significant milestone in India's space exploration efforts, showcasing ISRO's ability to deploy advanced satellites with precision and efficiency.
We also Published
- Cartesian Product
The cartesian product of two sets A and B is defined as a set formed by all the possible ordered pairs of elements from A and B, such that the first element comes from set A and the second element comes from set B. The cartesian product is denoted as A × B. Let a and b […] - Chemical Fertilizer vs. Organic Fertilizer
A popular topic among agriculture specialists and home gardeners these days is the furore on organic fertilizer vs. chemical fertilizer. Now each fertilizer certainly has its pros and cons, but before we delve deeper into that, let us first make a few definitions. What is organic fertilizer? Organic fertilizers are substances containing nutrients derived from […] - Physics: Motion in One Dimension
Explore the principles of physics through Motion in One Dimension. Learn the fundamentals and key concepts.
The ISRO's SSLV-D3 Launch with EOS-8 Satellite: A Game-Changer in Satellite Launch Technology
The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, represents a leap forward in satellite deployment technology. The D3 variant of the SSLV is particularly noteworthy for its rapid assembly capability, which allows for the entire launch vehicle to be ready within a week—a stark contrast to the 45 days required by other launch vehicles. This efficiency is a testament to ISRO's commitment to innovation and its ability to meet the growing demands of satellite deployment.
EOS-8: A Technological Marvel in Orbit
The EOS-8 satellite, weighing 175.5 kilograms, is now orbiting Earth at an altitude of 475 kilometers. This satellite is equipped with cutting-edge technology designed to enhance India's Earth observation capabilities. EOS-8's primary mission includes capturing high-resolution images and conducting detailed analysis of Earth's features such as oceans, mountains, ice caps, and forests. This data is invaluable for applications in environmental monitoring, disaster management, and national security.
Advanced Payloads: Enhancing Earth Observation and Beyond
The ISRO's SSLV-D3 mission carried three primary payloads, each serving a unique and critical function:
- Electro-Optical Infrared (EOIR) Payload: This advanced imaging system captures images in the mid-wave and long-wave infrared bands, making it essential for satellite-based surveillance, environmental monitoring, and wildfire detection.
- Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) Payload: This payload is designed to analyze wind patterns over ocean surfaces, assess soil moisture levels, detect floods, and study the cryosphere in the Himalayas. It showcases ISRO's ability to leverage remote sensing technologies for diverse applications.
- SiC UV Dosimeter: As part of the preparations for future space missions, such as Gaganyaan, this payload monitors ultraviolet radiation in space and serves as a high-dose alarm sensor for gamma radiation, ensuring astronaut safety.
ISRO's SSLV-D3: Implications for India's Space Program
The success of the SSLV-D3 mission is not just a feather in ISRO's cap but a significant step forward for India's space program. The ability to deploy small satellites rapidly and efficiently positions India as a key player in the global space industry. The SSLV's design and capabilities make it particularly suited for launching small satellites, which are increasingly in demand for commercial and scientific purposes.
A Vision for the Future
ISRO's ongoing advancements in space technology, as exemplified by the SSLV-D3 and EOS-8, are paving the way for future missions that will push the boundaries of what is possible. The integration of advanced technologies into small satellite platforms allows for more frequent and cost-effective launches, enabling a broader range of missions that can address global challenges.
Conclusion
The SSLV-D3 mission is a clear indicator of ISRO's leadership in space technology. With the successful deployment of the EOS-8 satellite, India has once again proven its ability to innovate and excel in the competitive field of space exploration. As ISRO continues to develop new technologies and expand its capabilities, the world can expect even more groundbreaking missions in the years to come.
RESOURCES
- ISRO set to launch EOS-8 satellite with SSLV-D3 today: When and where to watch? What are mission's objectives? | Latest News India - Hindustan Times
- ISRO launches satellite EOS-08 to predict natural calamities and disasters | - Times of India
- ISRO successfully launches third and final developmental flight SSLV-D3-EOS8 mission - The Economic Times
- ISRO launches SSLV: What is the aim behind developing Small Satellite Launch Vehicles? | Explained News - The Indian Express
- ISRO: Isro successfully launches earth observation satellite aboard SSLV-D3 - The Economic Times
- Isro's SSLV-D3 mission successful, EOS-08 and SR-0 Demosat satellites placed in orbit | India News - Times of India
- ISRO successfully launches SSLV-D3-EOS-08 from Sriharikota - CNBC TV18
- Countdown begins for ISRO's third and final developmental flight SSLV-D3-EOS8 mission - The Hindu
- SSLV-D3/EOS-08 Mission
- ISRO EOS 08 launch: ‘No deviation, mission accomplished,’ says Somanath | Hindustan Times






0 Comments