personalised cancer vaccine marks a turning point in oncology, aligning therapy with a patient's tumor profile and immune landscape. This approach blends cutting-edge mRNA chemistry with individual genomic data to train the immune system to recognize malignant cells while sparing healthy tissue. EnteroMix’s early chatter illustrates both potential and peril in equal measure.
In Russia, researchers frame EnteroMix as a milestone toward fully tailored cancer care, initially targeting colorectal cancer with plans for glioblastoma and melanoma. Yet early data invite caution, underscoring that promising results in a small cohort must be replicated and scrutinized before broader clinical adoption.
On This Page
Read More
EnteroMix Unveiled: The Promise and the Caution
EnteroMix sits at the crossroads of immunology and precision medicine, promising to reframe how cancer is treated. This section examines the bold claim of 100% efficacy in early trials, balancing mathematical optimism with the practical need for independent validation and long-term safety data.
In Russia, researchers frame EnteroMix as a milestone toward fully tailored cancer care, initially targeting colorectal cancer with plans for glioblastoma and melanoma. Yet early data invite caution, underscoring that promising results in a small cohort must be replicated and scrutinized before broader clinical adoption.
Efficacy signals in early trials
The announcement centers on an mRNA-based approach that reportedly shrinks aggressive tumours and slows growth, with claims of high effectiveness and a tolerable safety profile. The vaccine is described as safe for repeated use and adaptable to a patient’s RNA, which could enable personalised immune targeting without harsh chemotherapy-like toxicity.
However, the evidence rests on phase-1 findings from a modest group, and details such as trial design, endpoints, and independent verification remain forthcoming. While a 100% signal sounds compelling, readers should weigh optimism against typical early-phase uncertainties and the lack of long-term outcome data.
Safety and manufacturing notes
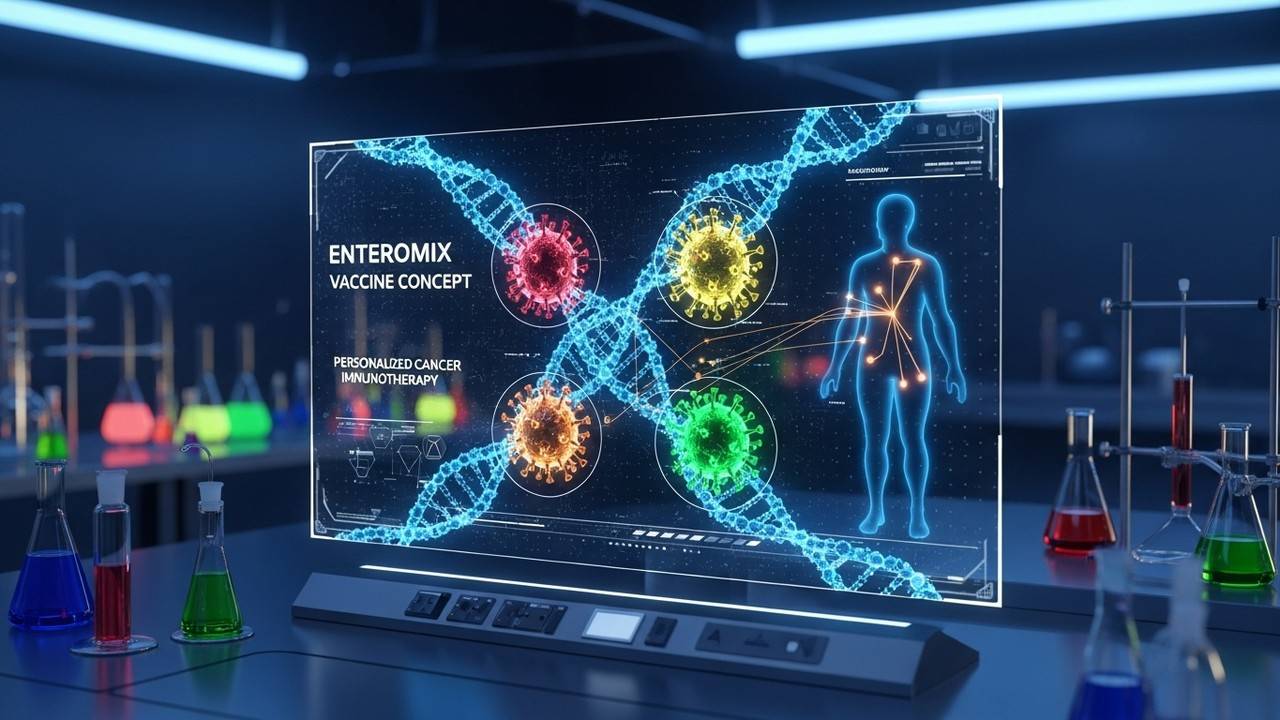
Officials describe EnteroMix as a vaccine that can be customised to individual RNA profiles, potentially reducing off-target effects. The platform reportedly leverages a four-virus strategy to stimulate immune activity while aiming to minimize collateral damage to healthy tissue.
Manufacturing considerations include scaling a personalised approach and ensuring consistency across patients. Regulatory scrutiny will hinge on reproducibility, real-world safety, and robust peer-reviewed publication to move beyond a promising concept into standard care.
Mechanism and Personalisation: How the Vaccine Works
Personalised cancer vaccines represent a frontier where biology and technology converge to teach the immune system to recognize tumours as targets. This section dissects how EnteroMix is positioned within that framework and what it could imply for future cancer therapies.
In brief, the EnteroMix approach blends mRNA vaccine technology with patient-specific molecular information to tailor an immune assault against tumours. The overarching aim is to generate a precise immune response that adapts to the evolving cancer landscape while preserving normal cells.
mRNA basis and four-virus strategy
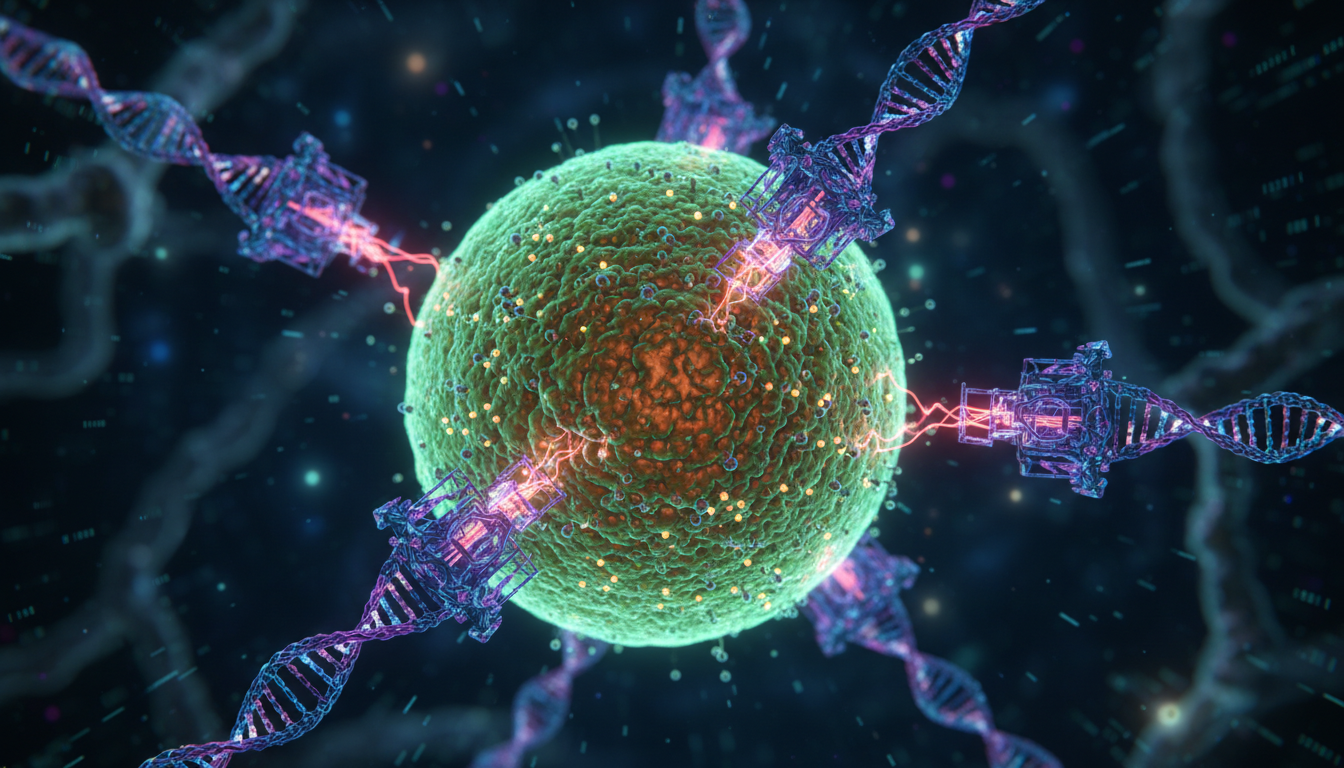
The platform builds on messenger RNA concepts popularized in infectious disease vaccines, repurposed to instruct cells to display tumour-associated proteins. The described four-virus cocktail is designed to broaden immune recognition and address heterogeneity within tumours, potentially improving response durability.
Vectors or virus-like components are used to present tumour signals to immune cells, prompting targeted cytotoxic activity. While this strategy is biologically plausible and grounded in existing vaccine science, its performance against diverse cancers remains to be validated in larger cohorts.
Self-tailoring to patient RNA
Tailoring to an individual’s RNA is at the heart of the personalised concept, aiming to align vaccine targets with each patient’s tumour fingerprint. If proven viable, this could reduce ineffective treatment and spare patients from broad-spectrum cytotoxic therapies.
Implementation challenges include rapid sequencing, data interpretation, and logistics to produce patient-specific formulations within clinically meaningful timelines. Success hinges on streamlined workflows, robust regulatory pathways, and transparent reporting of all safety and efficacy data across diverse populations.
Clinical Pathway and Global Implications
Progress from preclinical insight to patient care often travels a winding path. This section surveys the current stage of EnteroMix and what it could mean for global cancer treatment if validated in subsequent trials.
Early-phase momentum raises questions about generalisability, manufacturing scalability, and the speed with which regulatory bodies may evaluate personalised biologics. The implications extend beyond a single vaccine, hinting at a broader shift toward immune-based, tailored cancer therapies.
Phase I data and sample size
Phase I trials for EnteroMix reportedly enrolled a limited number of volunteers, providing preliminary signals of safety and activity. While small studies can illuminate potential, they cannot establish definitive efficacy or long-term outcomes, underscoring the need for larger, controlled studies to corroborate initial impressions.
Interpretation should also account for patient selection, tumour type distribution, and endpoints used in early testing. Transparent reporting will be essential to separate hype from substantiated medical advancement.
Regulatory and future applications
Regulatory review will hinge on reproducibility, manufacturing consistency, and comprehensive safety profiles across multiple cancer types. If proven effective, personalised vaccines could broaden to other tumours, potentially transforming how clinicians approach cancer with a patient-centric immunotherapy paradigm.
Beyond colorectal cancer, expansion to glioblastoma and melanoma signals a versatile roadmap. The field will watch closely for independent studies, standardized protocols, and real-world data that reveal true clinical benefit and cost-effectiveness across health systems.
Key Takeaways
Prospective advantages of a personalised cancer vaccine include targeted immune activation, potentially fewer side effects than conventional therapies, and the possibility of tailoring treatment to tumour biology. Nonetheless, substantial uncertainties remain, including the need for rigorous validation and scalable manufacturing.
What to watch next is the publication of peer-reviewed phase-appropriate results, independent replication across diverse patient groups, and a clear regulatory path that can transform a promising platform into reliable clinical practice. The coming months will be decisive for EnteroMix and the broader field of personalised cancer vaccines.
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Claimed efficacy | Reports of 100% efficacy in early phase need independent confirmation |
| Mechanism | mRNA platform with a four-virus strategy aiming for targeted immune attack |
| Personalisation | Tailored to each patient’s RNA profile for a customised immune response |
| Trial stage | Phase I with a small cohort; larger studies required for validation |
| Safety considerations | Reported safe with repeated use; long-term safety pending further data |
| Regulatory outlook | Awaiting peer-reviewed results and regulatory clearance for broader use |
We also Published
RESOURCES
- Personalized cancer vaccine design using AI-powered technologies
- When will patients see personalized cancer vaccines? — Harvard ...
- Personalized Vaccine for Liver Cancer Shows Promise in Clinical ...
- Thousands to trial personalised cancer vaccines
- Thousands of patients to access trials of personalised cancer vaccines
- Personalized Therapeutic Vaccine 'Steers' the Immune System to ...
- Personalized cancer vaccination is emerging: lessons learnt from ...
- Modified Personalized Cancer Vaccine Generates Powerful Immune ...
- Personalized Cancer Vaccine Proves Promising in a Phase 1 Trial ...
- UCLA Health launches clinical trial using personalized cancer ...




2 Comments